DIABETES and its management
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose), which is the main source of energy for our cells. Its impact on daily life can be significant, depending on the type of diabetes, how well it’s managed, and an individual’s lifestyle.
Here’s a breakdown of how diabetes can affect daily living:
🩸 1. Daily Management and Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring: People with diabetes often need to check their blood glucose multiple times a day using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
Medication and insulin: Those with type 1 diabetes (and some with type 2) must take insulin regularly. Timing and dosage are critical to prevent high (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia) blood sugar.
Meal planning: Careful attention to carbohydrate intake, portion sizes, and meal timing is necessary to maintain stable glucose levels.
🥗 2. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is essential. People with diabetes need to limit sugary foods, refined carbs, and processed snacks.
They may need to plan meals ahead, especially when eating out, to ensure foods align with their glucose management plan.
Regular hydration and portion control also become daily habits.
🏃 3. Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps control blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
However, it requires planning—exercise can lower blood sugar, so individuals must monitor levels before and after workouts and sometimes adjust meals or medication.
😓 4. Emotional and Mental Impact
Managing diabetes can be stressful and emotionally draining, leading to anxiety or “diabetes burnout.”
Fear of complications or sudden low blood sugar episodes (especially at night or while driving) can also impact mental health and daily confidence.
💼 5. Work and Social Life
People may need to plan around medication schedules, meal breaks, or glucose checks during work or social events.
Employers and friends may not always understand the condition, which can create feelings of isolation or stigma.
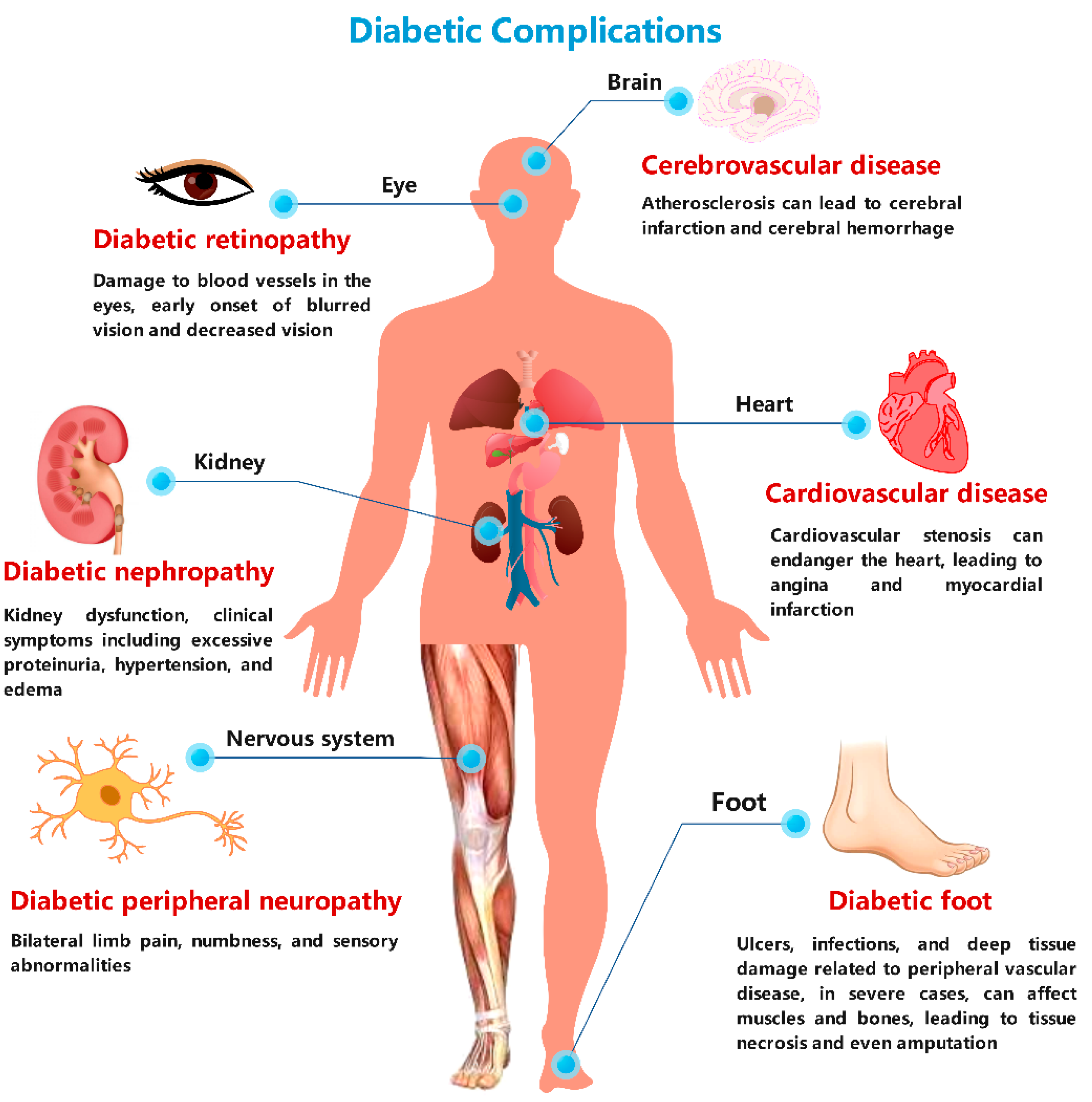
🦶 6. Long-term Health and Lifestyle Adjustments
Ongoing vigilance is needed to prevent complications such as heart disease, neuropathy, eye problems, and kidney disease.
Regular medical appointments (e.g., endocrinologists, dietitians, eye exams) become part of life.
Good sleep, stress management, and self-care routines are vital.
❤️ 7. Positive Adaptations
While diabetes requires discipline, many people live full, active lives by:
Learning to interpret their body’s signals.
Using modern tools like insulin pumps, smart CGMs, and diabetes apps.
Building strong support networks (family, healthcare teams, and online communities).
Be the first to add your comment

![Acute gastroenteritis [AGE] Acute gastroenteritis [AGE]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761888601_images_(1).jpg)
![HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure] HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761813352_bp.png)
