COPD and related issues
What is COPD?
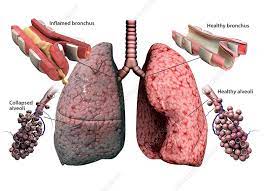
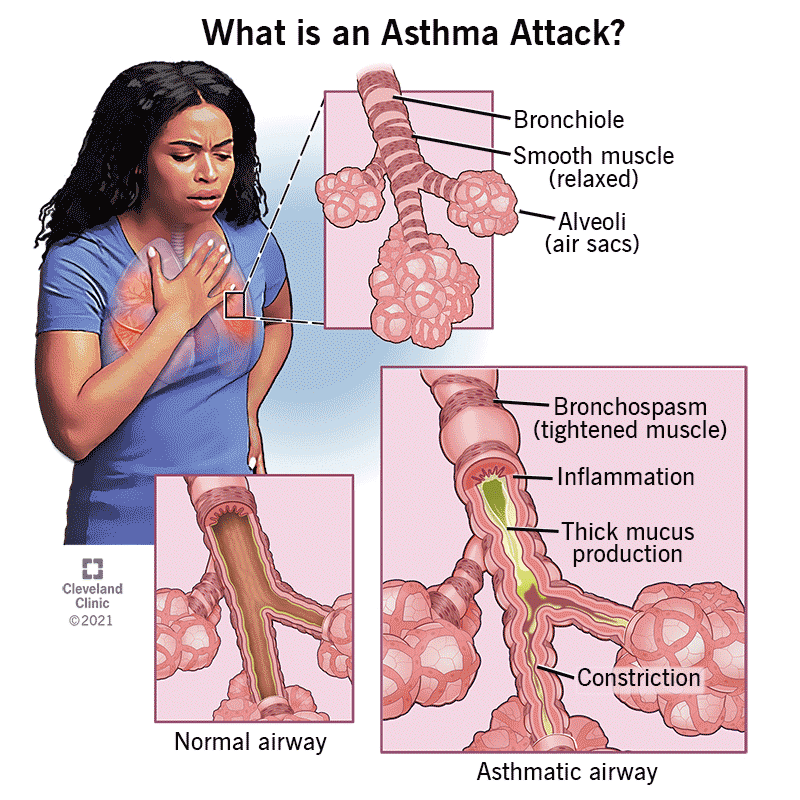
COPD is a chronic (long-term), progressive lung disease that makes it hard to breathe.
It includes two main conditions:
Chronic bronchitis – long-term inflammation of the airways, causing cough with mucus.
Emphysema – destruction of the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, reducing oxygen exchange.
🔍 Causes
Smoking (most common cause)
Long-term exposure to air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust
Genetic factors (like α₁-antitrypsin deficiency)
Frequent lung infections in childhood
⚠️ Symptoms
Persistent cough (often with sputum)
Shortness of breath (especially on exertion)
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Fatigue
Frequent respiratory infections
In later stages: weight loss, cyanosis (bluish lips/nails), and swelling in ankles
🧬 Pathophysiology (in simple terms)
Airway inflammation → narrowing of bronchi
Damage to alveoli → less oxygen exchange
Air gets trapped in lungs → hyperinflation
Reduced lung elasticity → breathing difficulty
🧪 Diagnosis
Spirometry (PFT): FEV₁/FVC ratio < 0.70 confirms airflow obstruction
Chest X-ray / CT scan: shows hyperinflated lungs
Arterial blood gas: to check oxygen & carbon dioxide levels
Alpha-1 antitrypsin test: for genetic form
💊 Treatment & Management
There is no cure, but symptoms can be managed:
1. Medications
Bronchodilators: e.g., salbutamol, tiotropium
Inhaled corticosteroids: reduce inflammation
Combination inhalers
Antibiotics: during infections
Oral steroids: for acute flare-ups
2. Oxygen therapy
For patients with low oxygen levels.
3. Pulmonary rehabilitation
Breathing exercises, nutrition advice, and fitness training.
4. Lifestyle changes
Stop smoking (most important!)
Avoid pollutants
Regular vaccinations (flu, pneumonia)
Balanced diet and hydration
5. Surgical options (severe cases)
Lung volume reduction surgery
Lung transplant
🔄 Complications / Related Issues
Respiratory infections (frequent bronchitis, pneumonia)
Pulmonary hypertension
Right heart failure (cor pulmonale)
Osteoporosis (from steroids or inactivity)
Anxiety & depression (due to chronic illness)
Acute exacerbations – sudden worsening of symptoms
❤️🩹 Prevention
Don’t smoke (or quit if you do)
Avoid passive smoke & polluted environments
Regular exercise
Early treatment of chest infections
Be the first to add your comment

![Acute gastroenteritis [AGE] Acute gastroenteritis [AGE]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761888601_images_(1).jpg)
![HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure] HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761813352_bp.png)
