CKD and its complications
CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease) and its Complications 🩺
🔹 What is CKD?
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) means the gradual and permanent loss of kidney function over months or years.
Kidneys normally filter waste, maintain fluid & electrolyte balance, and regulate blood pressure.
In CKD, these functions decline slowly, leading to accumulation of toxins in the body.
🔹 Stages of CKD (based on GFR – Glomerular Filtration Rate)
| Stage | GFR (mL/min/1.73m²) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | ≥90 | Kidney damage with normal function |
| Stage 2 | 60–89 | Mild reduction |
| Stage 3a | 45–59 | Mild to moderate reduction |
| Stage 3b | 30–44 | Moderate to severe reduction |
| Stage 4 | 15–29 | Severe reduction |
| Stage 5 | <15 | Kidney failure (End Stage Renal Disease – ESRD) |
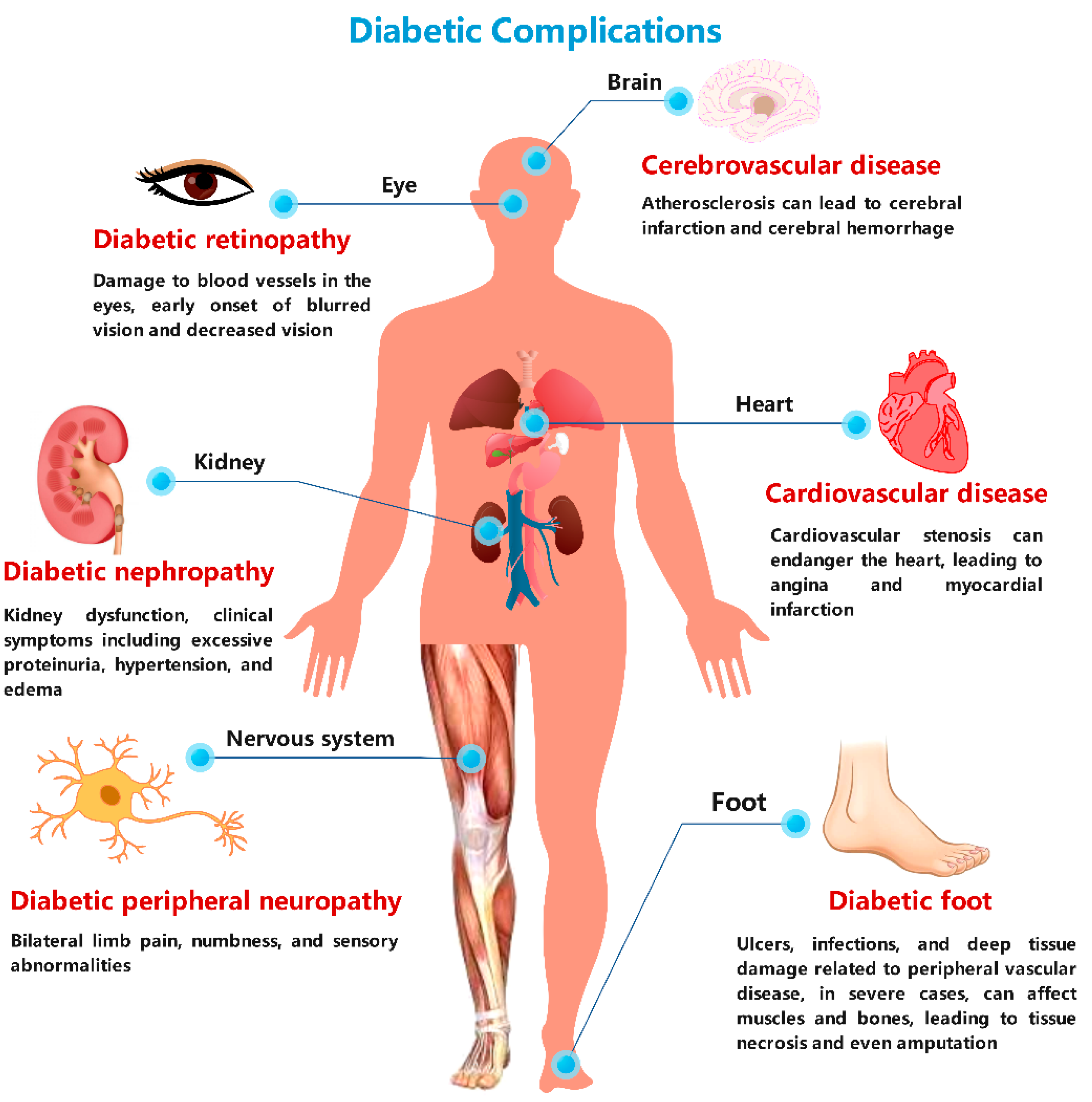
⚠️ Complications of CKD
1. Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance
Edema (swelling) – due to salt and water retention
Hyponatremia, hyperkalemia (high potassium – can cause cardiac arrest)
Metabolic acidosis – due to acid buildup
2. Cardiovascular Complications
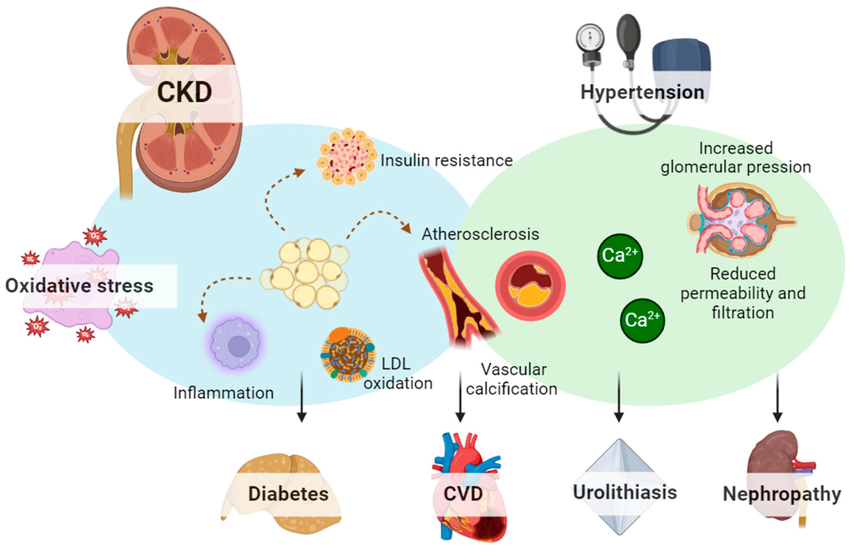
Hypertension – both cause and result of CKD
Heart failure due to fluid overload
Pericarditis (inflammation of the heart lining)
Atherosclerosis and stroke risk ↑
3. Anemia
Due to low erythropoietin (EPO) production by kidneys
Leads to fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath
4. Bone and Mineral Disorders
Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Leads to renal osteodystrophy (weak, brittle bones)
5. Uremia (Toxin Accumulation)
Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting
Itching (pruritus)
Confusion, seizures, coma in severe cases
6. Endocrine and Metabolic Issues
Insulin resistance
Dyslipidemia (↑ cholesterol/triglycerides)
Reproductive issues – impotence, menstrual irregularities
7. Infections
Lowered immunity → increased susceptibility to infections
8. Neurological Complications
Peripheral neuropathy (tingling, numbness in limbs)
Sleep disturbances
Cognitive decline
🩹 Prevention and Management
Control diabetes and hypertension
Low-salt, low-protein diet (as per stage)
Avoid nephrotoxic drugs (e.g., NSAIDs)
Treat anemia and bone disorders
Dialysis or kidney transplant in ESRD
Be the first to add your comment

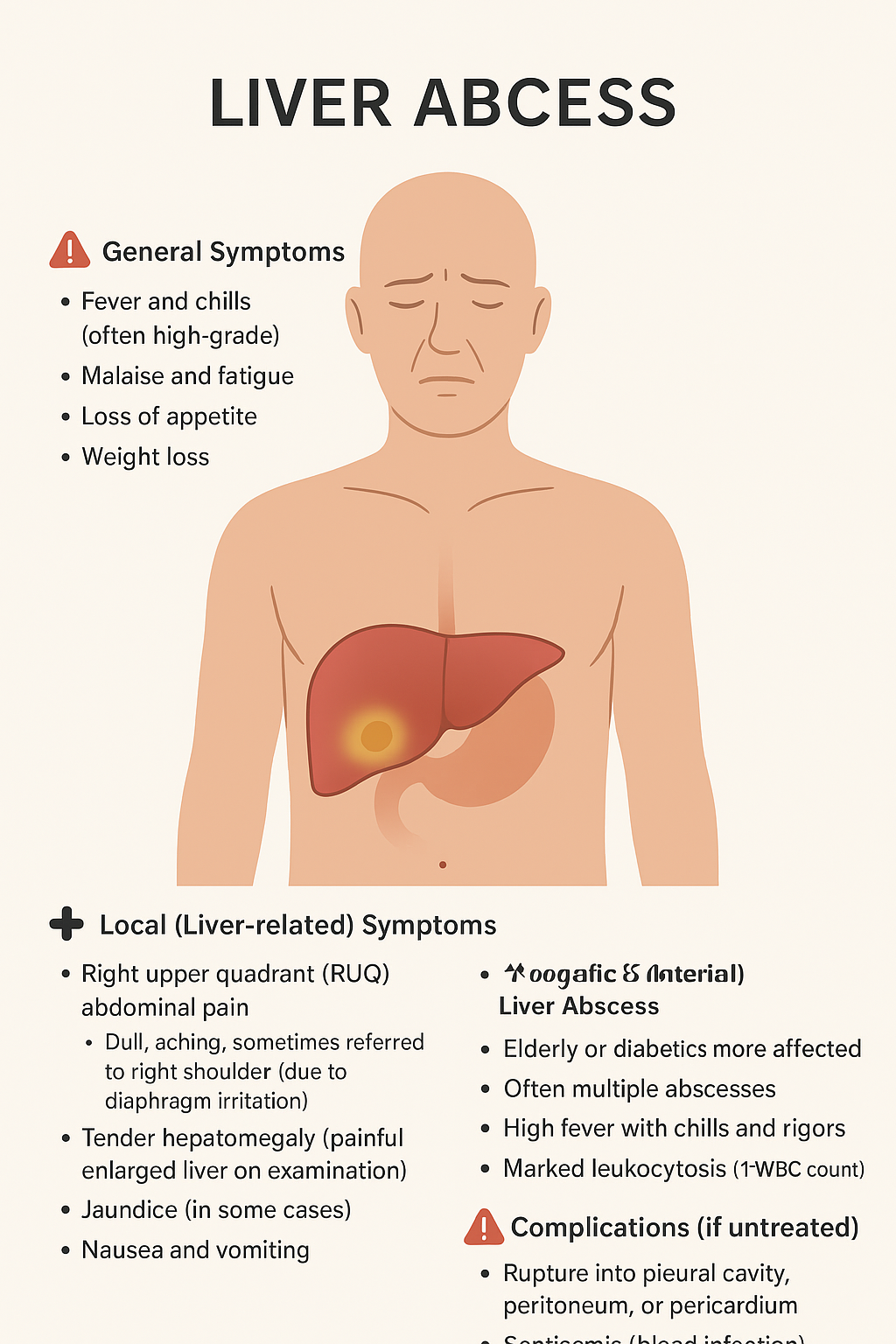
![Acute gastroenteritis [AGE] Acute gastroenteritis [AGE]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761888601_images_(1).jpg)
![HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure] HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761813352_bp.png)
