Acute Stroke and its management
Acute Stroke — Symptoms and Management 👇
🧠 What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients — causing brain cells to die within minutes.
Two main types:
Ischemic Stroke (≈ 85%) — due to blood clot or blockage in an artery.
Hemorrhagic Stroke (≈ 15%) — due to rupture of a blood vessel, causing bleeding in or around the brain.
⚠️ Symptoms of Acute Stroke
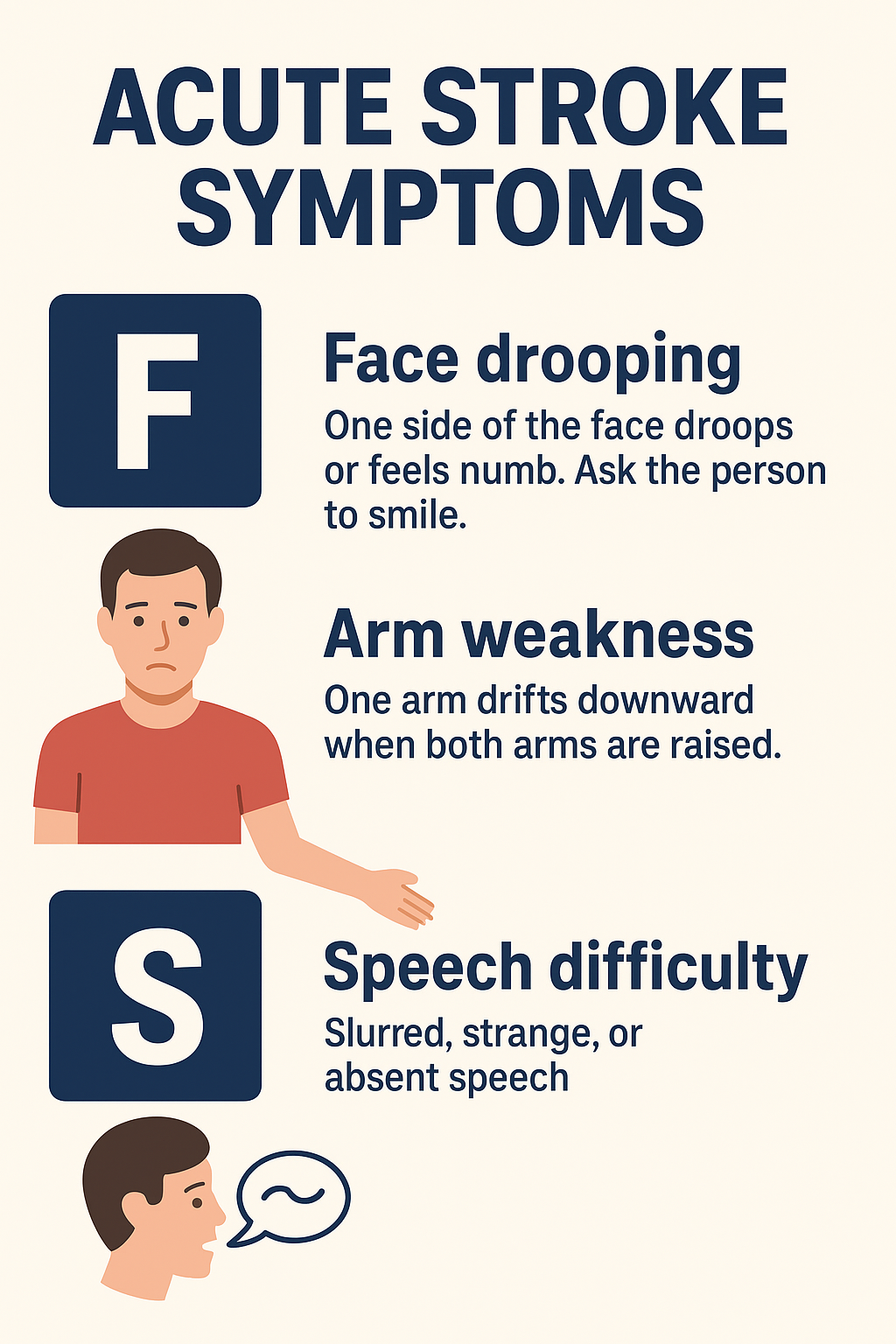
Remember the FAST rule:
| Mnemonic | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| F | Face drooping | One side of the face droops or feels numb. Ask the person to smile. |
| A | Arm weakness | One arm drifts downward when both arms are raised. |
| S | Speech difficulty | Slurred, strange, or absent speech. |
| T | Time to call emergency | Immediate medical help is crucial — “Time is Brain.” |
Other symptoms may include:
Sudden numbness or weakness (especially one-sided)
Sudden confusion or trouble understanding speech
Sudden vision problems (one or both eyes)
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination
Severe, sudden headache (especially in hemorrhagic stroke)
🏥 Emergency Management (Initial Steps)
Immediate Action:
Call emergency services (don’t wait for symptoms to improve).
Check airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
Do NOT give anything to eat or drink.
Note the time of symptom onset — crucial for treatment decisions.
💉 Hospital Management
1. Diagnosis
CT or MRI brain to distinguish ischemic vs hemorrhagic stroke.
Blood glucose, electrolytes, CBC, coagulation profile etc.
2. Ischemic Stroke Treatment
🩸 Goal: Restore blood flow quickly.
IV thrombolysis (tPA / Alteplase) if:
Within 4.5 hours of onset.
No contraindications (e.g., bleeding, recent surgery, etc.).
Mechanical thrombectomy (clot removal using catheter):
Within 6–24 hours for large vessel occlusion.
Supportive care:
Maintain airway, oxygen, and hydration.
Control blood sugar and blood pressure (avoid rapid drops).
Start antiplatelet (aspirin) after 24 hours (if no bleeding).
3. Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment
🩸 Goal: Control bleeding and reduce brain pressure.
Stop anticoagulants/antiplatelets if being used.
Manage blood pressure carefully (reduce if very high).
Surgical options:
Evacuation of hematoma if large or causing mass effect.
Repair of aneurysm or AVM if present.
Control intracranial pressure: Head elevation, osmotic diuretics (mannitol).
🔄 Post-Stroke Care & Prevention
Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy.
Prevent recurrence:
Control BP, diabetes, cholesterol.
Stop smoking, limit alcohol.
Continue antiplatelet (Aspirin/Clopidogrel) and statins as advised.
Be the first to add your comment

![Acute gastroenteritis [AGE] Acute gastroenteritis [AGE]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761888601_images_(1).jpg)
![HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure] HYPERTENSION [High Blood Pressure]](https://www.spiralshealth.com/public/images/blog/1761813352_bp.png)
